Dynamic wheel positioning
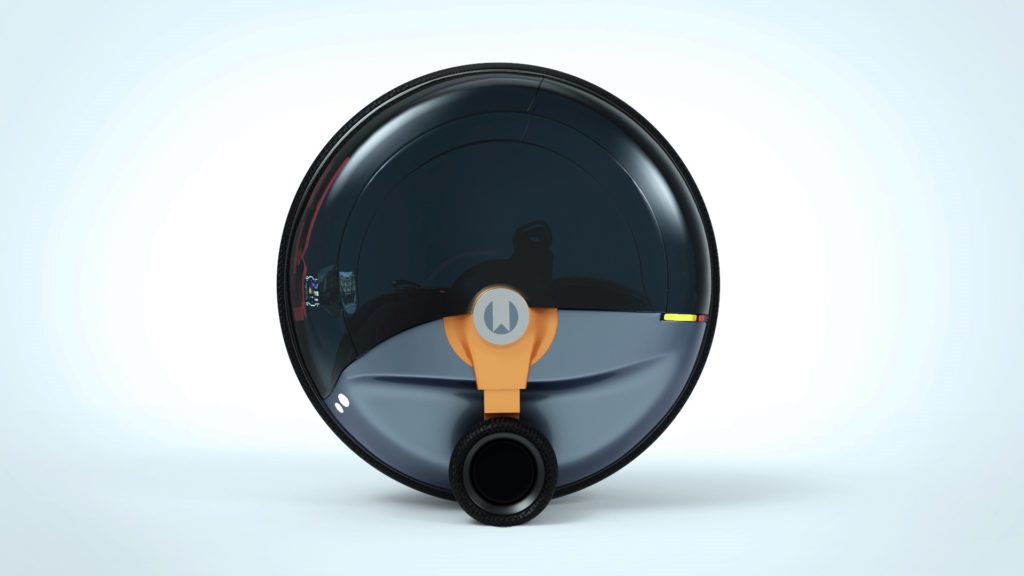

When aligned with the contact point of the monowheel, when starting a drive or when preparing to park, the side wheels can turn in the opposite direction, thus making the car swivel on the spot—similar to a bobcat or a Segway.
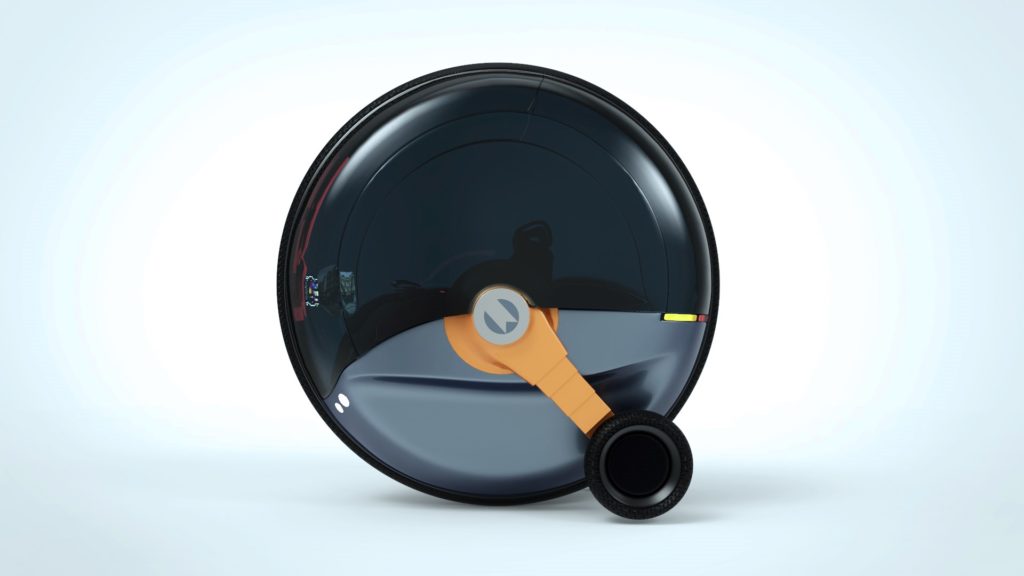

When accelerating, the side wheels move to the back end of the car using an extended hydraulic/electrical beam – forming a triangle wheel position.
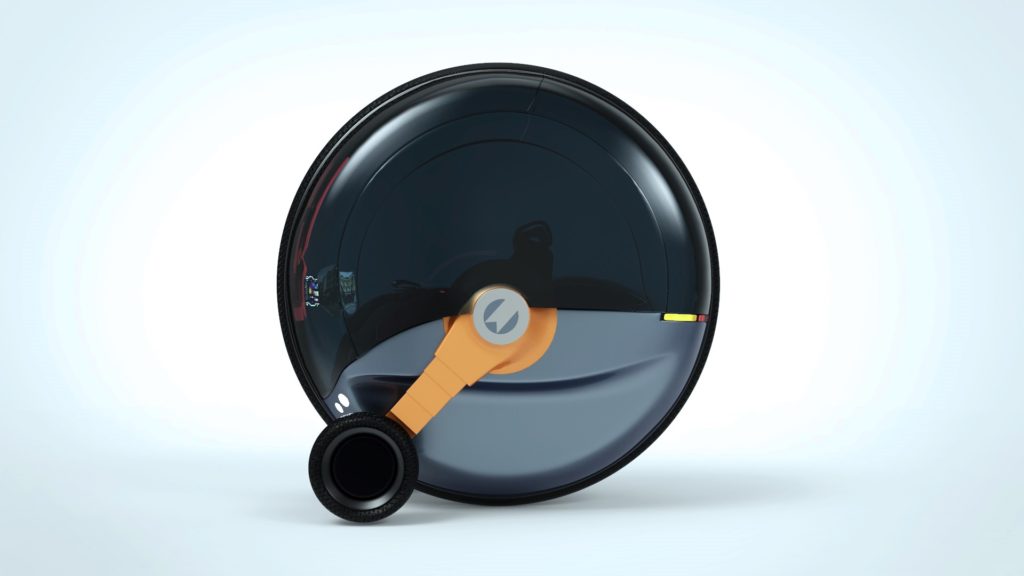

When deaccelerating, the side wheels move to the front end of the car using the hydraulic/electrical beam – to enhance road grip and shorten breaking distance and time.
Lean into curves
Upon turning, WATT deploys its servo-controlled tilt mechanism to execute a safe and comfortable turn.
The tilt system is designed to overcome gyroscopic stabilizing forces (used for straight motion) at turns using WATT’s own mass, much like a motorbike.